CaPGNN: Optimizing parallel graph neural network training with joint caching and resource-aware graph partitioning
Published in Neurocomputing, 2026
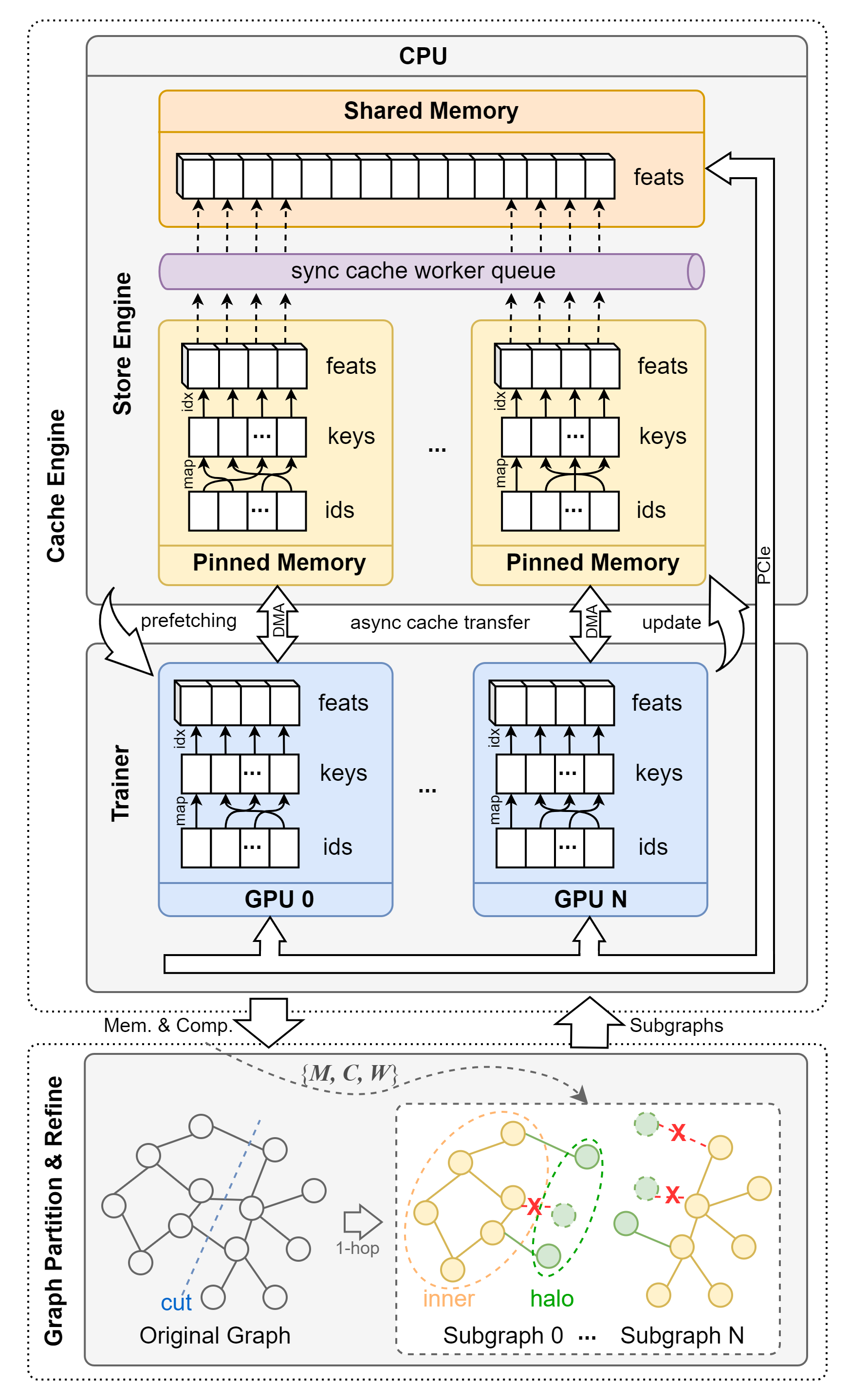
Graph-structured data is ubiquitous in the real world, and Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have become increasingly popular in various fields due to their ability to process such irregular data directly. However, as data scale, GNNs become inefficient. Although parallel training offers performance improvements, increased communication costs often offset these advantages. To address this, this paper introduces CaPGNN, a novel parallel full-batch GNN training framework on single-server with multi-GPU. Firstly, considering the fact that the number of remote vertices in a partition is often greater than or equal to the number of local vertices and there may exist many duplicate vertices, we propose a joint adaptive caching algorithm that leverages both CPU and GPU memory, integrating lightweight cache update and prefetch techniques to effectively reduce redundant communication costs. Furthermore, taking into account the varying computational and communication capabilities among GPUs, we propose a communication- and computation-aware heuristic graph partitioning algorithm inspired by graph sparsification. Additionally, we implement a pipeline to overlap computation and communication. Extensive experiments show that CaPGNN improves training efficiency by up to 18.98x and reduces communication costs by up to 99%, with minimal accuracy loss or even accuracy improvement in some cases. Finally, we extend CaPGNN to multi-machine multi-GPU environments.
Recommended citation: Xianfeng Song, Yi Zou, and Zheng Shi. "CaPGNN: Optimizing parallel graph neural network training with joint caching and resource-aware graph partitioning", in Neurocomputing, pp. 132978, 2026.
Download Paper | Download Code
